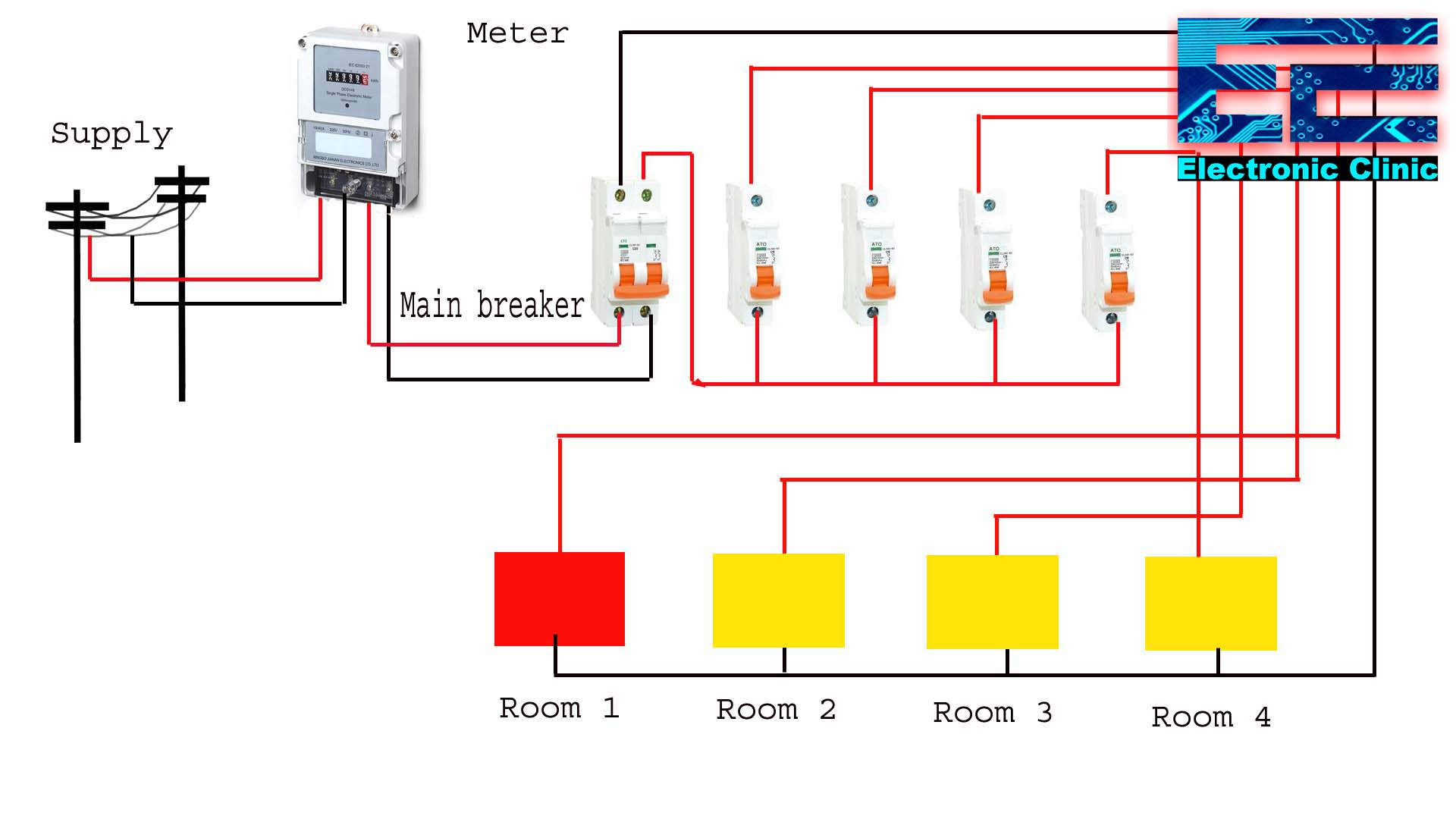
Smart Info About Why Use DC Circuit Breaker

Why DC Circuit Breakers? It's Not Just About Flipping a Switch!
Okay, so you're wondering about DC circuit breakers, huh? Maybe you're setting up a solar panel system, tinkering with electric vehicles, or just plain curious. Whatever the reason, it's a smart question. Think of DC circuit breakers as the guardians of your electrical kingdom — small but mighty protectors ready to spring into action when things go sideways.
Unlike their AC cousins that work with alternating current (think the power in your home outlets), DC circuit breakers are designed specifically for direct current systems. Direct current flows in one direction only, kind of like a one-way street for electrons. And that difference is crucial when it comes to safety and efficiency. Ignoring this is like putting diesel into a gasoline engine — you're not going to have a good time.
The main point here is safety. Electrical faults, like short circuits or overloads, can generate a ton of heat really quickly. If left unchecked, this heat can lead to fires, damaged equipment, and potentially much worse. A DC circuit breaker's job is to detect these faults and interrupt the current flow super-fast, preventing disaster. They are your first line of defense against electrical gremlins!
And let's be real, nobody wants a surprise electrical fire. Investing in quality DC circuit breakers is like buying an insurance policy for your electrical systems. You might not need it every day, but when you do need it, you'll be incredibly grateful it's there.
1. The Nitty-Gritty
Okay, let's get a little more technical, but don't worry, I'll keep it relatively painless. A DC circuit breaker is essentially an automatic switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after a fault is detected.
These breakers work using various mechanisms, typically involving thermal or magnetic tripping. A thermal breaker uses a bimetallic strip that bends when heated by excessive current, tripping the breaker. A magnetic breaker uses an electromagnet that pulls a latch when the current exceeds a predetermined level, also tripping the breaker. Regardless of the mechanism, the goal is the same: to stop the flow of current quickly and safely.
What's particularly important about DC circuit breakers is their ability to handle the unique challenges of interrupting direct current. DC doesn't have the natural zero-crossing point that AC has, making it more difficult to extinguish an arc when the breaker trips. Special design features are incorporated to ensure that the arc is quenched quickly and safely.
Think of it like this: AC is like a wave that naturally dips to zero, giving the breaker a chance to "reset." DC is like a constant stream; the breaker has to actively force the break. This requires robust construction and specific materials designed to handle the high voltages and currents often found in DC systems. It is not your regular switch!

Solar Power and DC Circuit Breakers
Solar power systems are practically synonymous with DC. Solar panels generate direct current, which then needs to be converted to alternating current for use in most homes and businesses. But before that conversion happens, DC circuit breakers play a vital role in protecting the solar panels, inverters, and other components.
Imagine a sunny day with your solar panels cranking out the amps. Now imagine a sudden surge of power due to a lightning strike or a faulty component. Without DC circuit breakers, that surge could fry your entire system, costing you a fortune in repairs and lost energy production. DC breakers are the unsung heroes keeping your solar investment safe and sound.
In solar installations, you'll typically find DC circuit breakers in multiple locations: between the solar panels and the inverter, and sometimes within the inverter itself. This layered protection ensures that any fault is quickly isolated, preventing cascading failures and minimizing downtime. It's all about redundancy and peace of mind.
And consider the long-term benefits. Regular maintenance and inspection of your DC circuit breakers can help prevent future problems and extend the lifespan of your entire solar system. It's a small investment that pays off big time in terms of reliability and performance. So next time you admire your solar panels, remember the little DC circuit breakers working tirelessly behind the scenes.
2. Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are another prime example of where DC circuit breakers are essential. EVs use high-voltage DC batteries to power their electric motors. These batteries can deliver a tremendous amount of current, making fault protection absolutely critical.
Inside an EV, DC circuit breakers protect the battery pack, the motor controllers, and other high-voltage components from overloads and short circuits. A fault in any of these areas could lead to a fire or explosion, so the breakers act as a crucial safety mechanism for both the vehicle and its occupants.
Think about it: you're driving down the road, and suddenly there's an electrical issue in the motor. Without a DC circuit breaker, the resulting surge could cause catastrophic damage to the motor controller, potentially leaving you stranded. The breaker trips, disconnecting the power and preventing further damage. You might be inconvenienced, but you're also safe.
Furthermore, DC circuit breakers are used in EV charging stations to protect both the vehicle and the grid from faults during the charging process. They ensure that the charging process is safe and reliable, preventing damage to the vehicle's battery or the electrical infrastructure. So, every time you plug in your EV, you're benefiting from the protection provided by these unsung heroes.
Resonant DC Circuit Breaker (a) Active, (b) Passive Download
Beyond Solar and EVs
While solar power and electric vehicles are prominent examples, DC circuit breakers are used in a wide range of other applications. They're found in telecommunications equipment, industrial control systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and even marine applications.
In telecommunications, DC power is often used to operate critical equipment like servers and network switches. DC circuit breakers protect these devices from power surges and short circuits, ensuring that communication networks remain operational even during power outages or other disruptions. Imagine if your cell phone service went down every time there was a minor power fluctuation — that's the kind of chaos DC breakers help prevent.
Industrial control systems rely on DC power for many automation and control functions. DC circuit breakers protect these systems from faults that could disrupt production processes, damage equipment, and even create hazardous conditions. They are essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of industrial operations.
Even in boats, DC circuit breakers play a vital role. Marine electrical systems often use DC power for lighting, navigation equipment, and other essential functions. DC breakers protect these systems from faults that could occur due to corrosion, water damage, or other factors common in marine environments. So, whether you're sailing the high seas or just tinkering in your garage, DC circuit breakers are likely working behind the scenes to keep you safe.
3. Choosing the Right DC Circuit Breaker
Selecting the right DC circuit breaker for your application is crucial for ensuring proper protection and performance. Several factors need to be considered, including the voltage and current rating of the circuit, the type of load being protected, and the environmental conditions.
First, make sure that the breaker's voltage and current rating match or exceed the maximum voltage and current in the circuit. Using a breaker with an insufficient rating could lead to overheating, failure, and even a fire. It's always better to err on the side of caution and choose a breaker with a slightly higher rating than you think you need.
Second, consider the type of load being protected. Some loads, like motors, draw a large inrush current when they start up. You'll need a breaker that can handle this inrush current without tripping unnecessarily. Other loads might be more sensitive to voltage fluctuations, requiring a breaker with a fast tripping speed.
Finally, think about the environment in which the breaker will be used. If it's exposed to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures, you'll need a breaker that's specifically designed for those conditions. Look for breakers with appropriate environmental ratings, such as IP65 for water and dust resistance. And remember, when in doubt, consult with a qualified electrician to ensure that you're choosing the right breaker for your needs. They are the professionals, after all!

Circuit Breaker Types Of Different
FAQ About DC Circuit Breakers
Got more questions? Of course, you do! Here are a few frequently asked questions about DC circuit breakers:
4. Question
Answer: No, absolutely not! AC and DC circuit breakers are designed for different types of current and have different interrupting capabilities. Using an AC breaker in a DC circuit could be dangerous and could result in the breaker failing to trip when needed, potentially leading to serious damage or injury.
5. Question
Answer: It's generally recommended to test your DC circuit breakers at least once a year. This can be done by manually tripping the breaker and then resetting it. If the breaker doesn't trip properly or feels sluggish, it may need to be replaced. Regular testing ensures that the breaker is functioning correctly and will protect your equipment in the event of a fault.
6. Question
Answer: Both DC circuit breakers and fuses are designed to protect circuits from overcurrent, but they work in different ways. A fuse is a one-time device that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a certain level. A DC circuit breaker, on the other hand, is a resettable device that can be tripped and reset multiple times. Fuses are generally cheaper, but circuit breakers offer more convenience and flexibility.