Recommendation Tips About What Voltage Is 5V

Dc 5 Volt Power Supply
Understanding 5V
1. What Exactly Does 5V Mean?
So, you're wondering, "What voltage is 5V?" Well, the answer might seem obvious, but let's dig a little deeper. 5V stands for 5 Volts, and voltage itself is basically the "push" that drives electric current through a circuit. Think of it like water pressure in a pipe. Higher voltage equals more pressure, meaning more current can flow. This 5V standard is ubiquitous in the world of electronics because its a sweet spot, providing enough power for many devices without being too high and frying everything. Think of it as the Goldilocks zone of power.
It's used to power a vast array of devices, from your trusty USB devices to the microcontrollers humming away inside your favorite gadgets. It's a standardized voltage for a reason — it provides a reliable and relatively safe level of power. Imagine if everything had its own unique voltage requirement; charging your phone would be a chaotic nightmare! 5V simplifies things, making it easier to design and use electronic components.
Now, lets be clear, the 'V' stands for Volts, named after Alessandro Volta, the Italian physicist who invented the voltaic pile, an early form of the battery. Voltage is a measure of electric potential difference, which, in simpler terms, is the amount of work required to move a unit of electric charge between two points. So, when you see 5V, you're looking at a standard measure of this electrical "push" that keeps our devices running smoothly. It's the unsung hero of the electronic world!
Think about it this way: your phone charger spits out 5V, your computer's USB ports supply 5V, and even some hobby electronics projects rely on this voltage level. It's a common language spoken by countless circuits and devices. So, next time you plug something into a USB port, remember that 5V is quietly working its magic, keeping your digital world powered up.
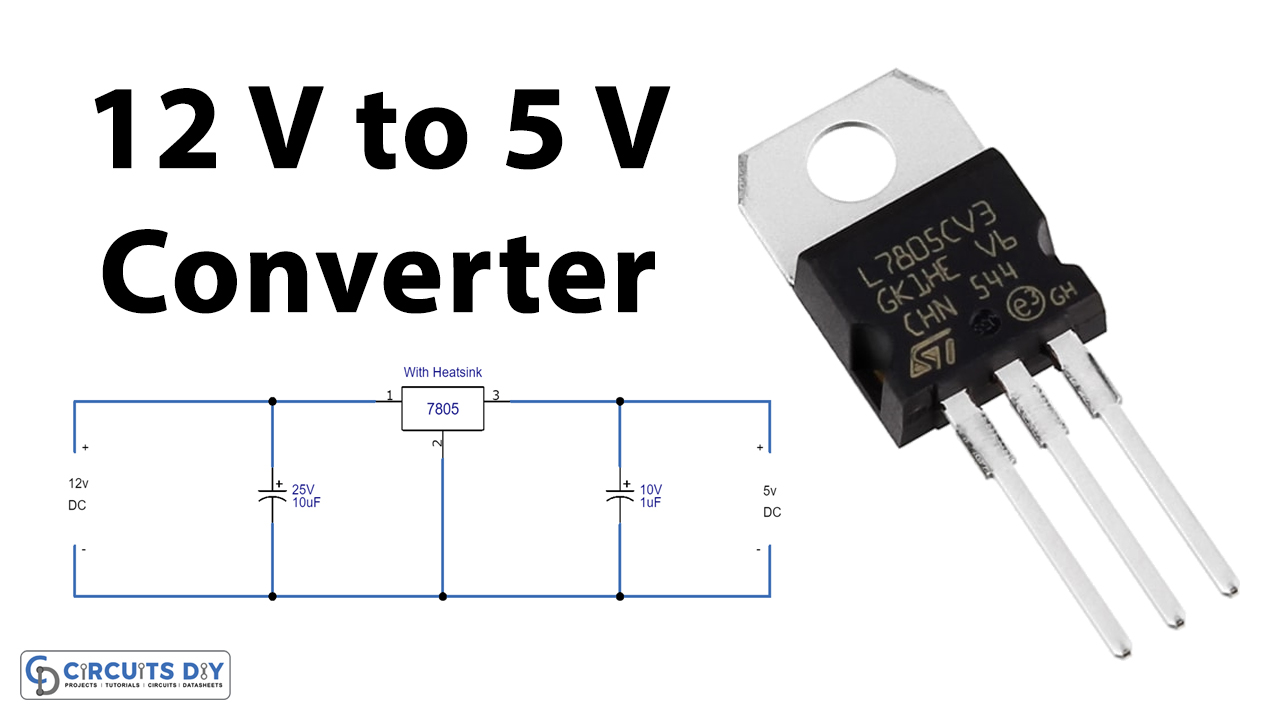
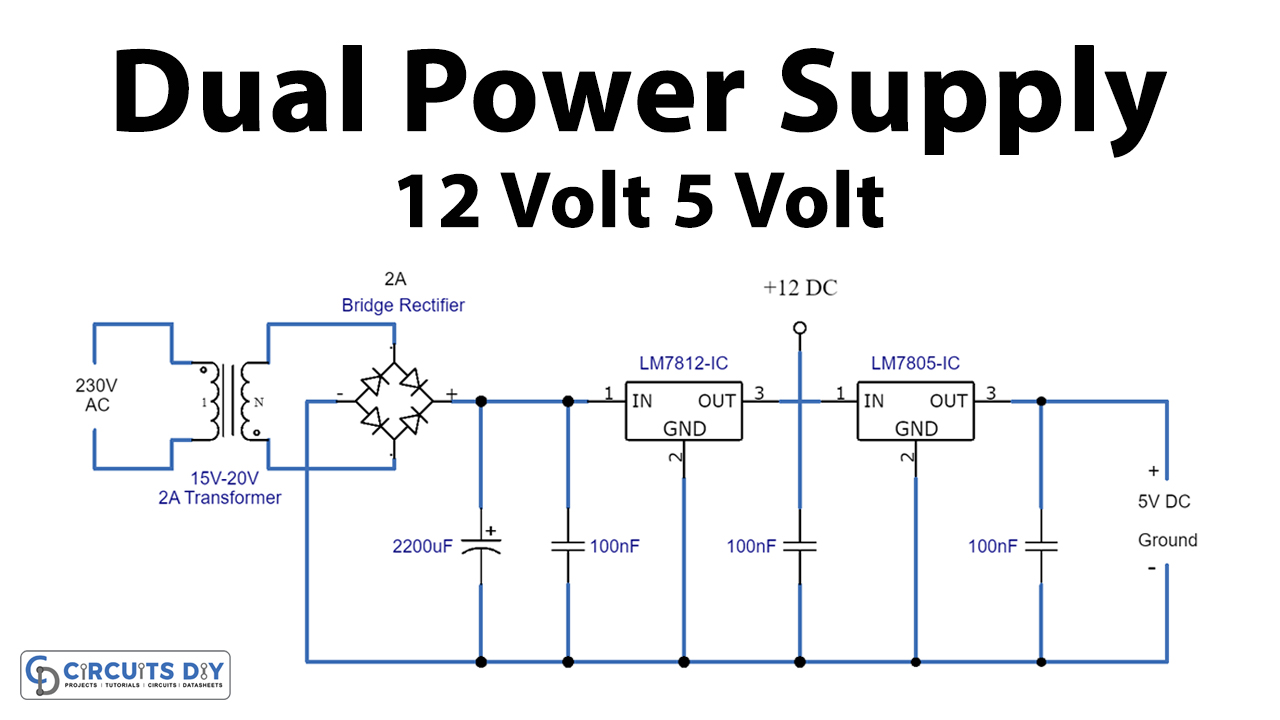
Where Do You Find 5V Power?
2. Common Sources of 5V
Okay, so we know 5V is important, but where do we actually find it? Well, it's practically everywhere in the electronic world! The most common source is definitely USB. Those handy ports on your computer, phone charger, and even your car provide a steady 5V supply. That's why you can charge so many different devices using the same USB cable — the 5V standard ensures compatibility.
Another frequent source is voltage regulators. These little components take a higher voltage (like the 12V from your computer's power supply) and step it down to a stable 5V. They're essential for keeping things running smoothly, preventing spikes and dips in voltage that could damage sensitive electronics. Think of them as the gatekeepers of your device's power supply.
Don't forget about power adapters! Many wall chargers output 5V directly, making them perfect for powering smaller devices like Raspberry Pis or Arduino boards. These adapters are designed to convert the higher voltage from your wall outlet (120V in the US, 230V in Europe) down to a safe and usable 5V level. They're lifesavers for anyone tinkering with electronics projects.
Finally, batteries can also be a source of 5V, although it usually requires a bit of tinkering. Multiple batteries can be connected in series to achieve the desired voltage, or a boost converter can be used to step up a lower voltage battery to 5V. This is commonly seen in portable devices and projects where wall power isn't readily available. The world is your 5V oyster!
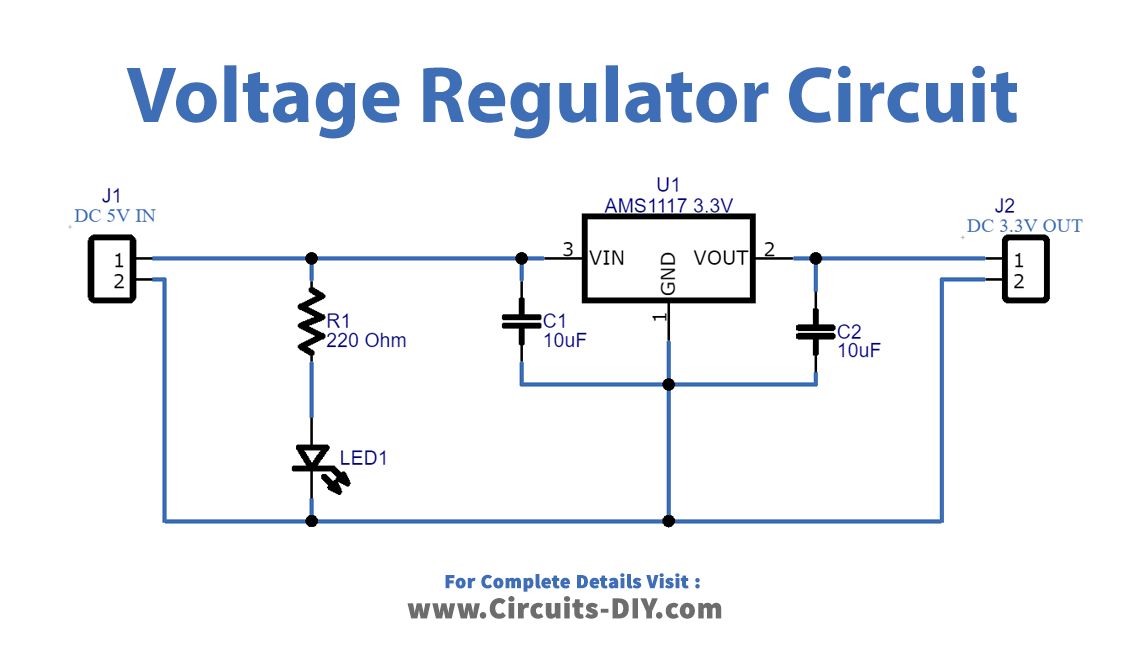
Power Supply Circuit 5v
Why 5V? What's So Special About It?
3. The Sweet Spot of Power
You might be pondering, "Why not 3.3V? Or 12V? Why is 5V so popular?" Well, it boils down to a few key factors. 5V strikes a great balance between power and safety. It's high enough to efficiently power a wide range of devices without being so high that it poses a significant risk of electrical shock or damage. It's the sweet spot of power delivery, as they say.
Also, 5V is historically significant. Many early microprocessors and digital logic circuits were designed to operate at 5V. This established a standard that has persisted over the years, making it easier to design and manufacture compatible components. Think of it as the legacy of the electronics world, passed down through generations of circuits.
Another reason is the availability of inexpensive and reliable voltage regulators that can easily convert higher voltages down to 5V. This makes it simple to integrate 5V power into a wide range of devices, regardless of their primary power source. It's a practical and cost-effective solution for many applications.
Furthermore, 5V is relatively easy to work with in terms of circuit design. It's a well-understood voltage level, and there are countless resources and tutorials available to help you design and troubleshoot 5V circuits. It's the friendly voltage that welcomes both beginners and experienced engineers alike.
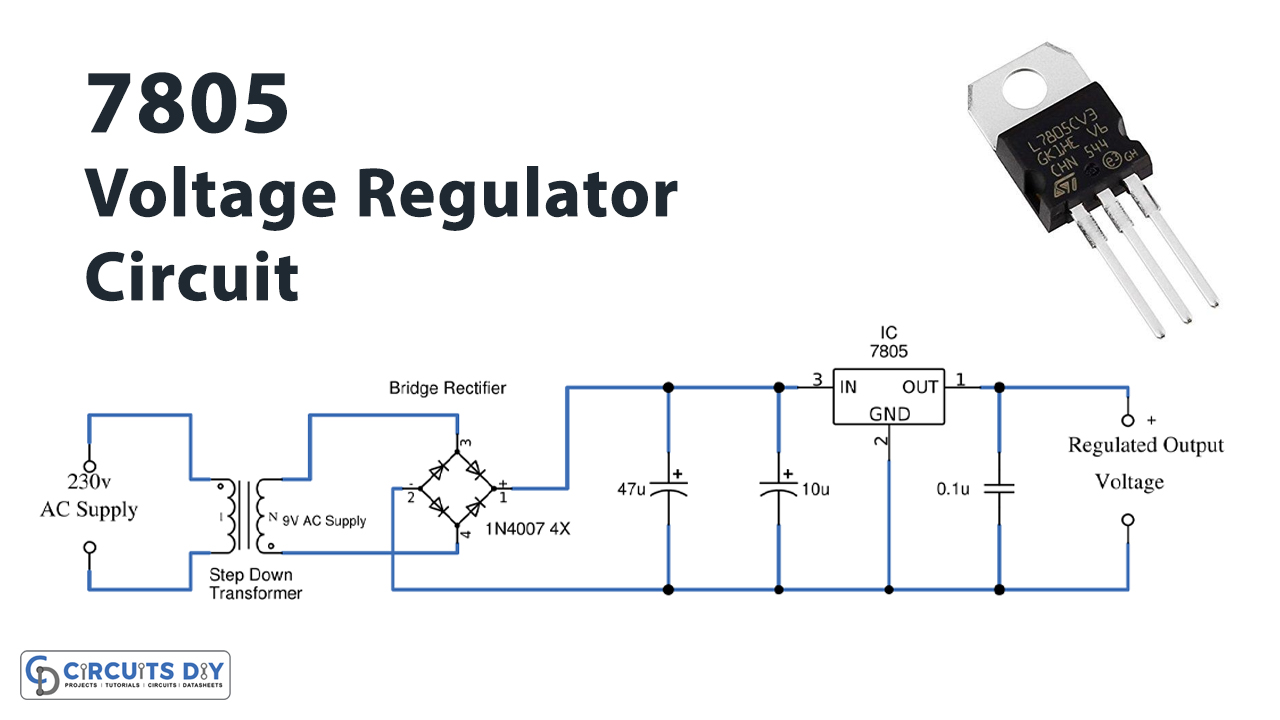
Voltage Control Circuits Design
Potential Issues with 5V
4. When Things Go Wrong
While 5V is generally safe and reliable, it's not without its potential issues. One common problem is voltage drop. This occurs when the voltage at the end of a long wire or cable is lower than the voltage at the source. This can happen due to the resistance of the wire, especially if the current draw is high. Imagine trying to drink through a really long straw; the water pressure decreases as it travels further.
Another issue is noise. Power supplies can sometimes generate electrical noise, which can interfere with sensitive electronic circuits. This noise can manifest as small fluctuations in voltage that can disrupt the operation of microcontrollers and other digital devices. Filtering capacitors are often used to smooth out these fluctuations and keep the voltage clean.
Overcurrent is another potential problem. If a circuit draws too much current from a 5V power supply, it can overload the supply and potentially damage it. This is why it's important to use appropriate fuses and current limiting resistors in your circuits. Think of it as preventing a dam from bursting by controlling the water flow.
Finally, be aware of polarity. Always double-check that you're connecting the positive and negative terminals correctly. Reversing the polarity can quickly destroy electronic components. It's a mistake that even experienced engineers can make, so always be cautious and double-check your wiring!

FAQ
5. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still got questions about 5V? No worries, we've got you covered!
Q: Can I use a 5V charger for a device that requires a slightly different voltage (e.g., 4.7V)?
A: Generally, a slight voltage difference like that (4.7V vs. 5V) is usually acceptable, especially if the device has its own internal voltage regulation. However, always check the device's specifications. Going significantly higher in voltage could damage the device.
Q: What happens if I accidentally connect a 12V power supply to a 5V device?
A: Catastrophic failure is highly likely. Applying 12V to a device designed for 5V will usually fry it instantly. The excess voltage will cause components to overheat and fail, potentially resulting in smoke, sparks, and a very unhappy device.
Q: Is 5V safe to touch?
A: Generally, yes, 5V is considered a low voltage and is not typically dangerous to touch under normal circumstances. However, it's always a good idea to exercise caution when working with electricity. Make sure your hands are dry, and avoid touching exposed wires if possible. Remember, even low voltages can be dangerous under certain conditions!