Ideal Info About What Is The Most Powerful Circuit Breaker

Type Of Circuit Breaker
Understanding Circuit Breakers
1. What exactly is a circuit breaker?
Okay, let's break it down (pun intended!). A circuit breaker is essentially a safety device designed to protect your electrical circuits from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. Think of it as a tiny, vigilant guardian watching over your wiring. When things get too hot to handle, it trips, cutting off the power supply to prevent potential fires or damage to your appliances. It's a much more convenient alternative to fuses, because you can simply reset them. Imagine replacing a fuse every time your toaster throws a tantrum — no fun!
Unlike fuses, which melt and need replacing after an overload, circuit breakers can be reset, making them reusable and a more sustainable option. This reset mechanism usually involves flipping a switch or pushing a button, bringing your circuit back to life and allowing you to continue using your electrical appliances. The ability to reset is a key advantage, as it saves time and money on replacements and provides a quick solution to temporary electrical issues. A fuse, by contrast, is a one-time-use safety device that must be discarded and replaced when it blows.
Now, you might be thinking, "Why not just let all the electricity flow freely?" Well, that's a recipe for disaster! Too much current can overheat wires, causing insulation to melt, leading to short circuits and potentially dangerous electrical fires. Circuit breakers act as a critical line of defense, preventing these hazardous scenarios and ensuring the safety of your home or building. They are a proactive measure that can protect both your property and your loved ones. Without circuit breakers, we'd be living on the edge of electrical mayhem!
Furthermore, different types of circuit breakers exist for various applications. Some are designed for residential use, protecting your home's circuits, while others are built for heavy-duty industrial purposes, safeguarding large machinery and equipment. Each type is calibrated to respond to specific current levels and designed to handle the unique demands of its environment. Understanding the different types and their applications is key to selecting the right circuit breaker for the job, ensuring optimal safety and performance in any electrical setup.

Defining "Most Powerful"
2. What does "powerful" even mean in this context?
When we talk about the "most powerful" circuit breaker, we aren't talking about one that can power a small city. It's more about its interrupting capacity — the maximum amount of fault current it can safely interrupt without exploding in a shower of sparks and melted metal. Think of it like this: it's not about how much electricity it lets through, but how much it can safely stop during a fault. A circuit breaker with a high interrupting capacity can handle larger surges of current, providing better protection against serious electrical problems. Choosing the right interrupting capacity is crucial for ensuring safety and preventing damage to electrical systems.
The interrupting capacity is usually measured in kiloamperes (kA). A higher kA rating means the circuit breaker can handle a more substantial short circuit current. For instance, a circuit breaker with a 10kA interrupting capacity can safely stop a fault current of 10,000 amps. This capability is vital in industrial and commercial settings where large electrical loads can produce significant fault currents. Selecting a circuit breaker with an adequate interrupting capacity prevents catastrophic failures and ensures that the breaker can effectively protect the electrical system in the event of a fault.
Another factor that contributes to the "power" or capability of a circuit breaker is its voltage rating. The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the circuit breaker can safely handle. Higher voltage applications, such as those found in industrial power distribution systems, require circuit breakers with correspondingly high voltage ratings. Using a circuit breaker with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to failure and create a dangerous situation. Therefore, selecting a circuit breaker with an appropriate voltage rating is paramount for safety and performance in any electrical setup.
Ultimately, the "most powerful" circuit breaker for a specific application depends on the specific electrical requirements. This includes factors such as the potential fault current, voltage levels, and the type of equipment being protected. There is no one-size-fits-all solution, and the selection process should be guided by a thorough understanding of the electrical system's characteristics and safety standards. Consulting with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer is essential to ensure that the appropriate circuit breaker is chosen, safeguarding against potential hazards and maximizing the reliability of the electrical system.

How Does A House Circuit Breaker Work Diagram
Industrial Giants
3. Who are the heavy hitters in the circuit breaker world?
In the industrial realm, where massive electrical loads are the norm, you'll find circuit breakers that are absolute beasts. These are typically molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) or insulated case circuit breakers (ICCBs) with incredibly high interrupting capacities. These aren't your average household breakers; they're designed to protect substantial electrical equipment and systems. They are engineered to withstand extreme conditions and operate reliably even in the most demanding environments. Their robust construction and advanced features make them indispensable for safeguarding critical industrial infrastructure.
MCCBs are widely used in industrial and commercial applications to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. They are available in a range of sizes and interrupting capacities to suit different needs. Their ability to be customized with various trip units and accessories makes them highly versatile. MCCBs are designed to provide reliable protection in challenging conditions, ensuring that electrical systems remain safe and operational. Their robust construction and ease of maintenance make them a popular choice for industrial facilities worldwide.
ICCBs are even more robust than MCCBs, offering higher interrupting capacities and increased durability. They are often used in large-scale industrial applications such as power plants and substations. ICCBs are designed to handle extremely high fault currents, providing maximum protection for critical equipment. Their sophisticated arc extinguishing mechanisms and advanced control features ensure that they can operate reliably even in the most demanding situations. ICCBs are an essential component of any industrial electrical system, providing peace of mind and ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Some examples of manufacturers known for producing these high-interrupting circuit breakers include Schneider Electric, Eaton, and Siemens. These companies invest heavily in research and development to create innovative circuit breaker technologies that meet the evolving needs of the industrial sector. Their products are rigorously tested to ensure that they meet the highest safety and performance standards. These manufacturers play a crucial role in keeping industrial electrical systems safe and reliable, contributing to the smooth operation of businesses around the globe. Selecting the right circuit breaker from a reputable manufacturer is essential for ensuring long-term performance and safety.
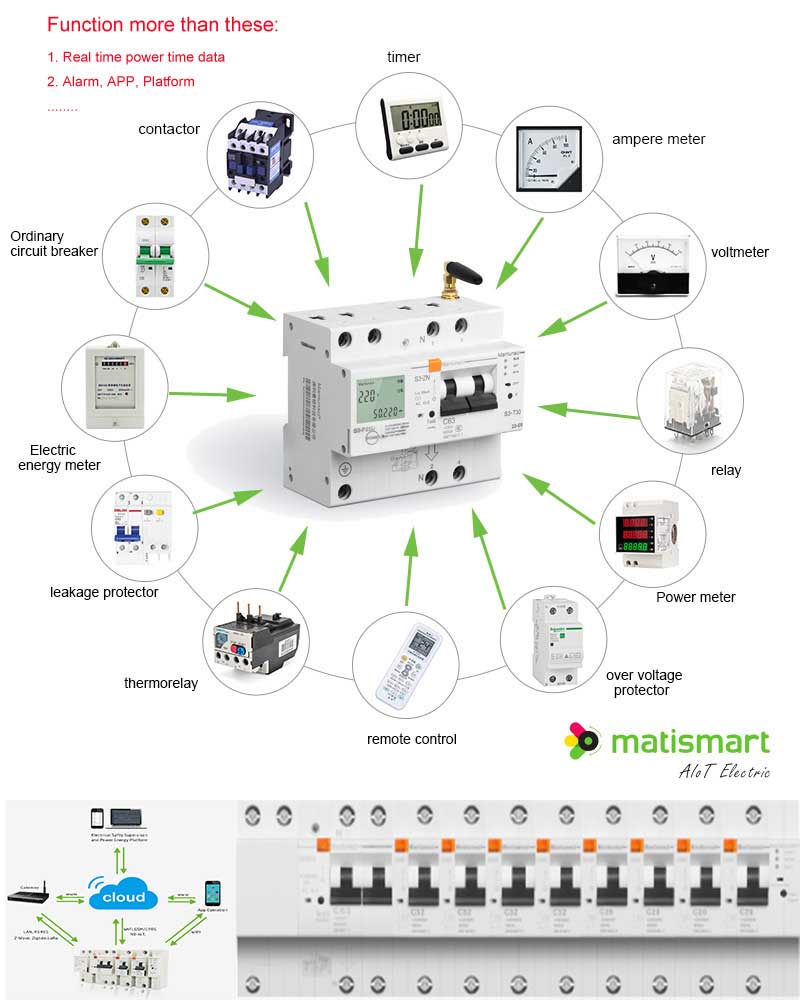
Benefits Of Smart Circuit Breakers Matismart
The Residential Champs
4. What about circuit breakers for our homes?
While your home's circuit breakers might not boast the same awe-inspiring interrupting capacity as their industrial counterparts, they are still essential for safety. Residential circuit breakers are typically single-pole or double-pole and are designed to protect circuits rated at 15, 20, or 30 amps. These breakers are designed to handle the electrical loads of everyday appliances and lighting, ensuring that your home's electrical system operates safely and reliably. Their quick response to overloads and short circuits prevents potentially dangerous situations from developing. Regular inspection and maintenance of residential circuit breakers is crucial for ensuring their continued effectiveness in protecting your home and family.
Arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) are a particularly important type of residential circuit breaker. AFCIs are designed to detect dangerous arc faults, which are electrical discharges that can occur when wires are damaged or insulation is frayed. These arc faults can generate high temperatures and potentially ignite nearby materials, leading to fires. AFCIs can quickly shut off the power to the affected circuit, preventing the fire from starting. They are a vital safety device for protecting your home from electrical fires, especially in areas where wiring is more likely to be damaged, such as bedrooms and living rooms. Installing AFCIs is a proactive step that can significantly reduce the risk of electrical fires in your home.
Ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) are another essential type of residential circuit breaker. GFCIs are designed to detect ground faults, which occur when electricity flows through an unintended path, such as a person's body. Ground faults can be extremely dangerous, causing severe electric shocks. GFCIs can quickly shut off the power to the affected circuit, preventing the shock. They are required in areas where water is present, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets, to protect against potential electrocution hazards. Ensuring that your home is equipped with GFCIs in these critical areas is essential for protecting yourself and your family from electrical shocks.
So, while residential circuit breakers might not be "powerful" in the same way as industrial breakers, they are perfectly suited for the specific electrical needs of your home. They provide reliable protection against overloads, short circuits, arc faults, and ground faults, ensuring the safety and well-being of your family. Regular inspection and maintenance of your home's circuit breakers, along with the installation of AFCIs and GFCIs in appropriate areas, are crucial steps in maintaining a safe and electrically sound home environment. By understanding the different types of residential circuit breakers and their functions, you can take proactive steps to protect your home and family from electrical hazards.

Choosing the Right Breaker
5. How do I pick the right circuit breaker for the job?
The key takeaway here is that there's no single "most powerful" circuit breaker in a universal sense. The ideal choice depends entirely on the specific application. Consider the voltage, current, and interrupting capacity requirements of the circuit you're protecting. Also, think about the environment: is it a dusty industrial setting or a cozy living room? Are there any specific codes or regulations that you need to adhere to? All of these factors will play a role in determining the right circuit breaker for the job. Consulting with a qualified electrician is highly recommended, as they can assess your specific needs and recommend the appropriate circuit breaker for your situation.
When selecting a circuit breaker, it's crucial to understand the difference between standard circuit breakers, AFCIs, and GFCIs. Standard circuit breakers provide basic protection against overloads and short circuits, while AFCIs protect against arc faults and GFCIs protect against ground faults. Depending on the application, you may need to use a combination of these different types of circuit breakers to provide comprehensive protection. For example, in a bathroom, you would typically use a GFCI outlet to protect against ground faults near water sources, while an AFCI circuit breaker would protect the entire circuit from arc faults. Understanding the specific functions of each type of circuit breaker is essential for ensuring that your electrical system is properly protected.
Another important consideration is the interrupting capacity of the circuit breaker. The interrupting capacity should be high enough to safely handle the maximum fault current that could occur in the circuit. If the interrupting capacity is too low, the circuit breaker could fail to interrupt the fault current, leading to a potentially dangerous situation. To determine the appropriate interrupting capacity, you should consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer who can perform a fault current study. This study will analyze the electrical system and determine the maximum fault current that could occur at various points in the circuit. Based on this analysis, you can select a circuit breaker with an appropriate interrupting capacity.
Ultimately, choosing the right circuit breaker is a critical safety decision that should not be taken lightly. Consulting with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer is highly recommended, as they can provide expert guidance and ensure that you select the appropriate circuit breaker for your specific needs. By carefully considering the voltage, current, interrupting capacity, environmental factors, and applicable codes and regulations, you can ensure that your electrical system is properly protected and that you and your family are safe from electrical hazards.
